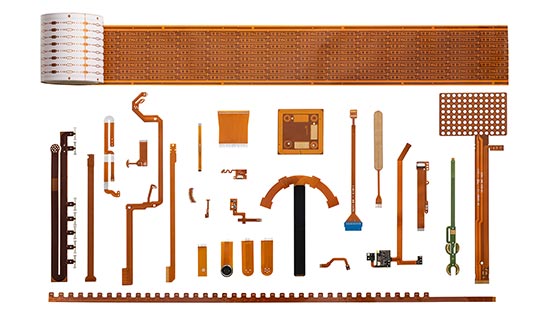
A flexible PCB (flexible printed circuit board, flex PCB, or just FPCB) is a printed circuit technology using a flexible substrate instead of a rigid one (generally FR4). The flexible substrate can have different thicknesses and the most common materials used are polyimide (also known by the name Kapton®), PET, and PEN.
Other materials can also be used, including woven fibres such as fibreglass or LCP for RF applications.